先日、コマンドラインでGoogle検索する方法を紹介しました。今回は、コマンドラインでGoogle翻訳する方法を紹介しましょう。
Translate Shellを使えば、コマンドラインから機械翻訳サービスを利用することができます。Google翻訳のほか、Bing翻訳、Yandex Translateなどにも対応しています。
ちょっとした翻訳なら、ブラウザを開かずにコマンドでやったほうが便利ですよ。翻訳された文を発音させることもできます。
Translate Shellのインストール
ディストリビューションによってはパッケージ化されているのですが、古いもバージョンだと動かなくなっていたりするので、最新のものをダウンロードしましょう。以下のコマンドで、「/usr/local/bin/trans」にダウンロードし、実行可能にします。
sudo wget git.io/trans -O /usr/local/bin/trans
sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/trans実行にはgawkコマンドとfribidiコマンドが必要です。また、mplayerもしくはmpg123コマンドがあれば翻訳文を発音させることが可能です。以下の手順でインストールします。
Ubuntu 16.04およびDebian 9の場合
sudo apt -y install gawk libfribidi-bin mplayerFedora 26の場合
sudo dnf -y install gawk fribidi mpg123CentOS 7の場合
sudo yum -y install gawk fribidi mpg123Translate Shellで翻訳する
他の言語から日本語へ
以下のように言語コードを指定して実行します。言語コードは一覧にまとめられています。
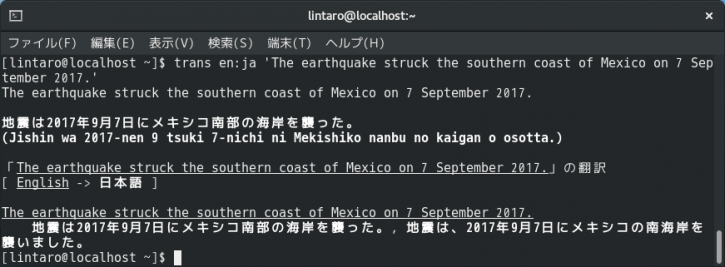
trans en:ja 'The earthquake struck the southern coast of Mexico on 7 September 2017.'ちょっとごちゃごちゃしてますね。「-b」オプションを追加すれば、訳文だけ表示されます。
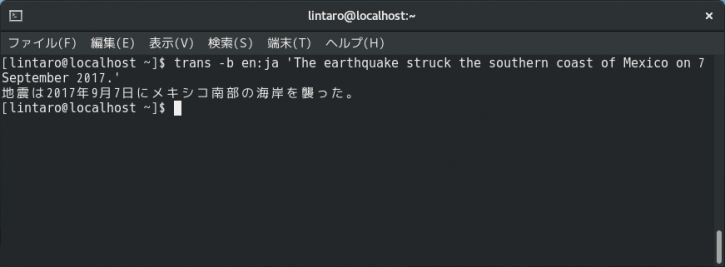
trans -b en:ja 'The earthquake struck the southern coast of Mexico on 7 September 2017.'これなら、訳文をパイプでさらに別のプログラムに送ったりもできますね。さらに「-p」オプションで訳文を発音させることができます。
trans -b -p en:ja 'The earthquake struck the southern coast of Mexico on 7 September 2017.'日本語から他の言語へ
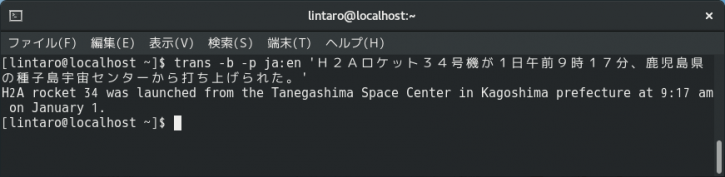
以下は日本語から英語に変換し、発音させる例です。
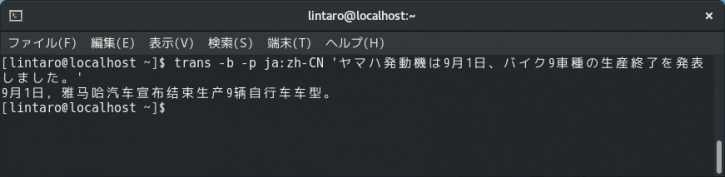
trans -b -p ja:en 'H2Aロケット34号機が1日午前9時17分、鹿児島県の種子島宇宙センターから打ち上げられた。'もちろん、英語以外に変換することもできます。以下は中国語(簡体字)に変換する例です。
trans -b -p ja:zh-CN 'ヤマハ発動機は9月1日、バイク9車種の生産終了を発表しました。'なお、デフォルトではGoogle翻訳が用いられます。「-e bing」を指定することで、Bing翻訳に切り替えることができます。
trans -b -p -e bing ja:en '天気を見るためにブラウザに切り替えたり、わざわざスマホを見たりするのも面倒です。コマンドで天気を確認できるようにしておきましょう。'まとめ
ここで紹介した以外にも、さまざまなオプションがあります。Translate Shellのサイトにさまざまな実行例が掲載されているので、自分に合った使い方を探してみてください。
transコマンドのヘルプ
Usage: trans [OPTIONS] [SOURCE]:[TARGETS] [TEXT]...
Information options:
-V, -version
Print version and exit.
-H, -help
Print help message and exit.
-M, -man
Show man page and exit.
-T, -reference
Print reference table of languages and exit.
-R, -reference-english
Print reference table of languages (in English names) and exit.
-L CODES, -list CODES
Print details of languages and exit.
-U, -upgrade
Check for upgrade of this program.
Display options:
-verbose
Verbose mode. (default)
-b, -brief
Brief mode.
-d, -dictionary
Dictionary mode.
-identify
Language identification.
-show-original Y/n
Show original text or not.
-show-original-phonetics Y/n
Show phonetic notation of original text or not.
-show-translation Y/n
Show translation or not.
-show-translation-phonetics Y/n
Show phonetic notation of translation or not.
-show-prompt-message Y/n
Show prompt message or not.
-show-languages Y/n
Show source and target languages or not.
-show-original-dictionary y/N
Show dictionary entry of original text or not.
-show-dictionary Y/n
Show dictionary entry of translation or not.
-show-alternatives Y/n
Show alternative translations or not.
-w NUM, -width NUM
Specify the screen width for padding.
-indent NUM
Specify the size of indent (number of spaces).
-theme FILENAME
Specify the theme to use.
-no-theme
Do not use any other theme than default.
-no-ansi
Do not use ANSI escape codes.
Audio options:
-p, -play
Listen to the translation.
-speak
Listen to the original text.
-player PROGRAM
Specify the audio player to use, and listen to the translation.
-no-play
Do not listen to the translation.
Terminal paging and browsing options:
-v, -view
View the translation in a terminal pager.
-pager PROGRAM
Specify the terminal pager to use, and view the translation.
-no-view
Do not view the translation in a terminal pager.
-browser PROGRAM
Specify the web browser to use.
Networking options:
-x HOST:PORT, -proxy HOST:PORT
Use HTTP proxy on given port.
-u STRING, -user-agent STRING
Specify the User-Agent to identify as.
Interactive shell options:
-I, -interactive, -shell
Start an interactive shell.
-E, -emacs
Start the GNU Emacs front-end for an interactive shell.
-no-rlwrap
Do not invoke rlwrap when starting an interactive shell.
I/O options:
-i FILENAME, -input FILENAME
Specify the input file.
-o FILENAME, -output FILENAME
Specify the output file.
Language preference options:
-l CODE, -hl CODE, -lang CODE
Specify your home language.
-s CODE, -sl CODE, -source CODE
Specify the source language.
-t CODES, -tl CODE, -target CODES
Specify the target language(s), joined by '+'.
Other options:
-no-init
Do not load any initialization script.
See the man page trans(1) for more information.
コメント