「Linuxコマンドまとめ」カテゴリでは、Linuxのコマンドについて、基本的な実行例とオプションを分かりやすくまとめます。
「ls」はファイル情報を出力するコマンドです。Linuxで最も頻繁に使われるコマンドでしょう。
端末を開いて、ただ「ls」とだけ実行すれば、以下のようにファイルの一覧が出力されます。
$ ls
examples.desktop テンプレート ドキュメント ピクチャ 公開
ダウンロード デスクトップ ビデオ ミュージックこれが基本ですが、オプションを追加することで、ファイル名以外の情報を確認したり、表示する情報を変えたり、出力順を並べ替えたりできるようになります。
lsコマンドの主なオプション7選
-a : .(ドット)で始まるファイルも含めて表示する
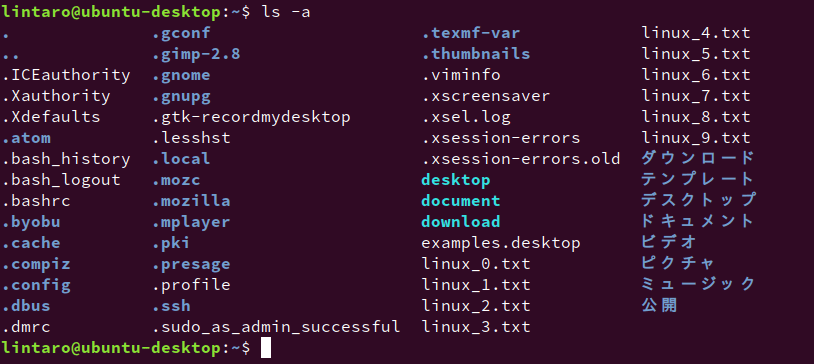
ls -aLinuxでは、通常の使用ではユーザーが変更しないファイルを、.(ドット)で始まるファイル名で保存します。ドットで始まるファイルは「ドットファイル」と呼ばれます。アプリケーションの設定やキャッシュなどが、自動的にドットファイルあるいはディレクトリに保存されていきます。lsコマンドは通常、このドットファイルを一覧に表示しません。
「-a」オプションを使うと、このドットファイルを一覧に含めることができます。以下は、ホームディレクトリで実行した時の出力例です。
さまざまなアプリが、ドットファイル、あるいはドットで始まるディレクトリに設定を書き込んでいるのが分かります。動作に不具合が出た場合に、このドットファイルやディレクトリを削除したり、設定を変更する場合にユーザー自身で編集するということもあります。たとえば、「.bashrc」を編集して環境変数を追加したり、「.ssh」ディレクトリにSSHで使う鍵を生成したりといった作業を行う場合です。そういう時、この「-a」オプションが活躍します。
-l : ファイルの詳細情報を表示する
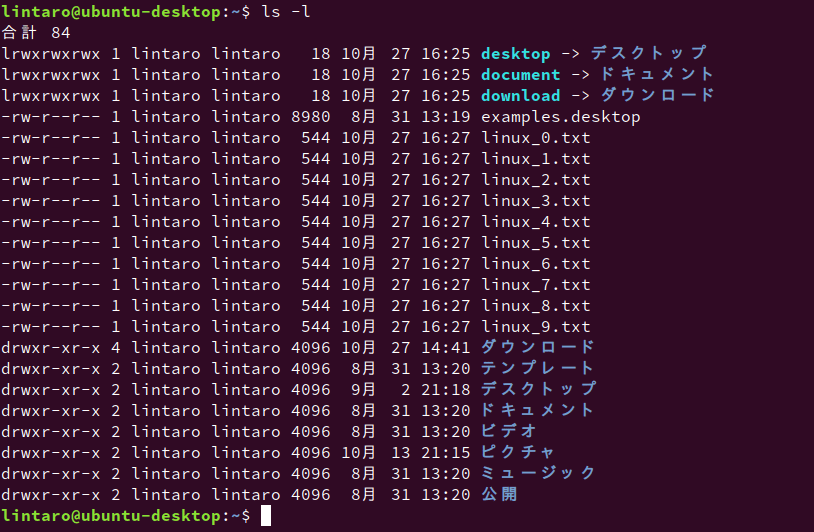
ls -l「-l」オプションを使うと、ファイルの詳細情報を出力します。
各行の左から、以下の順でファイルの情報が表示されています。
- ファイルタイプとパーミション
- 一番左の1文字がファイルタイプを表します(-:ファイル、d:ディレクトリ、l:シンボリックリンク など)。
- ハードリンク数
- 所有者
- 所有グループ
- サイズ
- 最終変更時刻
- ファイル名
なお、シンボリックリンクの場合は、「->」の後ろにリンク先が表示されます。
-d : ディレクトリの内部ではなくディレクトリ自体の情報を出力する
ls -d「a」で始まるファイルの詳細一覧表示をしたくて、以下のように実行したとします。
ls -l a*この時、aで始まるファイルだけでなくディレクトリが存在した場合、以下のような出力になります。
$ ls -l a*
-rw-r--r-- 1 lintaro lintaro 0 10月 27 15:31 a_file
a_dir:
合計 0
-rw-r--r-- 1 lintaro lintaro 0 10月 27 15:32 test_0
-rw-r--r-- 1 lintaro lintaro 0 10月 27 15:32 test_1
-rw-r--r-- 1 lintaro lintaro 0 10月 27 15:32 test_2
-rw-r--r-- 1 lintaro lintaro 0 10月 27 15:32 test_3
-rw-r--r-- 1 lintaro lintaro 0 10月 27 15:32 test_4
-rw-r--r-- 1 lintaro lintaro 0 10月 27 15:32 test_5
-rw-r--r-- 1 lintaro lintaro 0 10月 27 15:32 test_6
-rw-r--r-- 1 lintaro lintaro 0 10月 27 15:32 test_7
-rw-r--r-- 1 lintaro lintaro 0 10月 27 15:32 test_8
-rw-r--r-- 1 lintaro lintaro 0 10月 27 15:32 test_9「a_dir」というディレクトリが存在したため、その中にあるファイルの詳細も表示されました。こうではなく、ディレクトリ「a_dir」そのものの詳細情報を表示したい場合が多いでしょう。そういう時に使うのが「-d」オプションです。以下のように実行します。
$ ls -ld a*
drwxr-xr-x 2 lintaro lintaro 4096 10月 27 15:32 a_dir
-rw-r--r-- 1 lintaro lintaro 0 10月 27 15:31 a_fileこれで、期待通りの出力になりました。なお、この例の通り、オプションを複数指定するときは「-l -d」としなくても「-ld」のように、まとめて指定することもできます。
-h : ファイルサイズを分かりやすく表示
ls -lh「-l」オプションで詳細を表示すると、ファイルサイズは「バイト」で表示されます。これだと大きなファイルのサイズが分かりにくいですが、「-h」オプションをつけることで人間にも分かりやすい表示にしてくれます。「-l」と組み合わせて以下のように使います。
$ ls -lh /var/log/*.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 32K 10月 2 22:57 /var/log/Xorg.0.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 26K 9月 18 00:49 /var/log/Xorg.1.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 26K 9月 17 18:04 /var/log/Xorg.2.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 140K 10月 26 01:43 /var/log/alternatives.log
-rw-r----- 1 root adm 455 10月 27 16:51 /var/log/apport.log
-rw-r----- 1 syslog adm 1.2M 10月 27 17:12 /var/log/auth.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 6.8K 10月 27 11:25 /var/log/boot.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 63K 11月 22 2014 /var/log/bootstrap.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 6.9M 10月 26 01:43 /var/log/dpkg.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 13K 10月 12 09:38 /var/log/fontconfig.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 6.8K 10月 2 18:14 /var/log/gnustep-back-common.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2.1K 10月 27 11:25 /var/log/gpu-manager.log
-rw-r----- 1 syslog adm 971K 10月 27 16:57 /var/log/kern.log
-rw-r----- 1 syslog adm 629K 10月 27 17:12 /var/log/mail.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 11月 12 2016 /var/log/pm-powersave.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 11月 12 2016 /var/log/pm-suspend.log
-rw-r----- 1 syslog adm 0 10月 4 00:09 /var/log/repowerd.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 4.5M 10月 17 19:45 /var/log/vbox-install.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 702 10月 2 23:08 /var/log/wvdialconf.logこのように、「K(キロバイト)」「M(メガバイト)」「G(ギガバイト)」といった単位で表示されるようになります。
-t : タイムスタンプでソートする
ls -t新しいものから古いものにソートして出力します。新たに更新されたファイルを確認する時などに便利です。
$ ls -lt
合計 0
-rw-r--r-- 1 lintaro lintaro 0 10月 25 23:23 file_c
-rw-r--r-- 1 lintaro lintaro 0 10月 24 21:03 file_b
-rw-r--r-- 1 lintaro lintaro 0 10月 23 12:31 file_a以下のように、パイプで「head」コマンドへ送り、最近更新されたログファイルを確認するといった使い方もできます。
$ ls -lt /var/log | head
合計 34240
-rw-r----- 1 syslog adm 1169249 10月 27 17:49 auth.log
-rw-r----- 1 syslog adm 648037 10月 27 17:49 mail.err
-rw-r----- 1 syslog adm 648037 10月 27 17:49 mail.log
-rw-r----- 1 syslog adm 1405544 10月 27 17:49 syslog
-rw-r----- 1 syslog adm 993879 10月 27 17:37 kern.log
-rw-r----- 1 root adm 1411 10月 27 17:35 apport.log
-rw-rw-r-- 1 root utmp 128640 10月 27 11:25 wtmp
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 6936 10月 27 11:25 boot.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2139 10月 27 11:25 gpu-manager.log-S : サイズでソートする(大きいものから)
ls -Sサイズの大きいものから小さいものにソートして出力します。
$ ls -lS
合計 8200
-rw-r--r-- 1 lintaro lintaro 4256211 10月 27 17:52 file_b
-rw-r--r-- 1 lintaro lintaro 2187858 10月 27 17:52 file_a
-rw-r--r-- 1 lintaro lintaro 1942851 10月 27 17:53 file_c-F : ファイルの性質を表す文字をファイル名の末尾に追加する
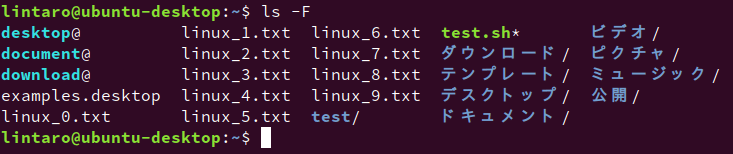
ls -Fディレクトリの場合は「/」、実行可能ファイルの場合は「*」、シンボリックリンクの場合は「@」をファイル名の末尾に追加します。
最近のLinuxシステムではファイルの性質により色分けして表示されますが、色では判別しにくい場合は役に立つでしょう。
パス名展開との組み合わせ
ファイル名やディレクトリ名には、bashによるパス名の展開を使って指定することができます。以下は実行例です。
# カレントディレクトリにあるファイルを一覧表示(ドットファイルを除く)
ls -ld *
# カレントディレクトリにあるドットファイルを一覧表示(「.」と「..」を含む)
ls -ld .*
# カレントディレクトリにあるドットファイルを一覧表示(「.」と「..」を除外)
ls -ld .[^.]*
# ホームディレクトリにある拡張子が2文字のファイルを一覧表示
ls -ld ~/*.??
# ホームディレクトリにある「File」または「file」をファイル名に含むファイルを一覧表示
ls -ld ~/*[Ff]ile*
# /etcにある小文字アルファベットで始まらないファイルを一覧表示
ls -ld /etc/[^a-z]*
# ユーザー「lintaro」のホームディレクトリにある拡張子が「txt」のファイルを一覧表示
ls -ld ~lintaro/*.txt
# /usr/bin/ または /usr/sbin にある a で始まるファイルを一覧表示
ls -ld /usr/{bin,sbin}/a*詳しくは、以下の記事をご覧ください。

lsのヘルプ
使用法: ls [オプション]... [ファイル]...
List information about the FILEs (the current directory by default).
Sort entries alphabetically if none of -cftuvSUX nor --sort is specified.
Mandatory arguments to long options are mandatory for short options too.
-a, --all . で始まる要素を無視しない
-A, --almost-all . および .. を一覧表示しない
--author -l と合わせて使用した時、各ファイルの作成者を表示する
-b, --escape 表示不可能な文字の場合に C 形式のエスケープ文字を表示する
--block-size=SIZE scale sizes by SIZE before printing them; e.g.,
'--block-size=M' prints sizes in units of
1,048,576 bytes; see SIZE format below
-B, --ignore-backups do not list implied entries ending with ~
-c with -lt: sort by, and show, ctime (time of last
modification of file status information);
with -l: show ctime and sort by name;
otherwise: sort by ctime, newest first
-C list entries by columns
--color[=WHEN] colorize the output; WHEN can be 'always' (default
if omitted), 'auto', or 'never'; more info below
-d, --directory list directories themselves, not their contents
-D, --dired generate output designed for Emacs' dired mode
-f do not sort, enable -aU, disable -ls --color
-F, --classify append indicator (one of */=>@|) to entries
--file-type likewise, except do not append '*'
--format=WORD across -x, commas -m, horizontal -x, long -l,
single-column -1, verbose -l, vertical -C
--full-time like -l --time-style=full-iso
-g -l と同様だがファイル所有者を表示しない
--group-directories-first
group directories before files;
can be augmented with a --sort option, but any
use of --sort=none (-U) disables grouping
-G, --no-group in a long listing, don't print group names
-h, --human-readable with -l and/or -s, print human readable sizes
(e.g., 1K 234M 2G)
--si likewise, but use powers of 1000 not 1024
-H, --dereference-command-line
follow symbolic links listed on the command line
--dereference-command-line-symlink-to-dir
follow each command line symbolic link
that points to a directory
--hide=PATTERN do not list implied entries matching shell PATTERN
(overridden by -a or -A)
--indicator-style=WORD append indicator with style WORD to entry names:
none (default), slash (-p),
file-type (--file-type), classify (-F)
-i, --inode print the index number of each file
-I, --ignore=PATTERN do not list implied entries matching shell PATTERN
-k, --kibibytes default to 1024-byte blocks for disk usage
-l 詳細リスト形式を表示する
-L, --dereference シンボリックリンクのファイル情報を表示するときは
リンクそのものではなくリンク参照先のファイル
情報を表示する
-m 要素のリストをカンマで区切り、一行に詰め込む
-n, --numeric-uid-gid like -l, but list numeric user and group IDs
-N, --literal print entry names without quoting
-o like -l, but do not list group information
-p, --indicator-style=slash
append / indicator to directories
-q, --hide-control-chars print ? instead of nongraphic characters
--show-control-chars show nongraphic characters as-is (the default,
unless program is 'ls' and output is a terminal)
-Q, --quote-name enclose entry names in double quotes
--quoting-style=WORD use quoting style WORD for entry names:
literal, locale, shell, shell-always,
shell-escape, shell-escape-always, c, escape
-r, --reverse ソート順を反転させる
-R, --recursive 子ディレクトリを再帰的に一覧表示する
-s, --size ブロック単位で各ファイルサイズを表示する
-S sort by file size, largest first
--sort=WORD sort by WORD instead of name: none (-U), size (-S),
time (-t), version (-v), extension (-X)
--time=WORD with -l, show time as WORD instead of default
modification time: atime or access or use (-u);
ctime or status (-c); also use specified time
as sort key if --sort=time (newest first)
--time-style=STYLE with -l, show times using style STYLE:
full-iso, long-iso, iso, locale, or +FORMAT;
FORMAT is interpreted like in 'date'; if FORMAT
is FORMAT1<newline>FORMAT2, then FORMAT1 applies
to non-recent files and FORMAT2 to recent files;
if STYLE is prefixed with 'posix-', STYLE
takes effect only outside the POSIX locale
-t ファイル更新時間で新しい順にソートする
-T, --tabsize=COLS タブ幅を 8 の代わりに COLS にする
-u with -lt: sort by, and show, access time;
with -l: show access time and sort by name;
otherwise: sort by access time, newest first
-U do not sort; list entries in directory order
-v natural sort of (version) numbers within text
-w, --width=COLS set output width to COLS. 0 means no limit
-x list entries by lines instead of by columns
-X sort alphabetically by entry extension
-Z, --context print any security context of each file
-1 list one file per line. Avoid '\n' with -q or -b
--help この使い方を表示して終了する
--version バージョン情報を表示して終了する
The SIZE argument is an integer and optional unit (example: 10K is 10*1024).
Units are K,M,G,T,P,E,Z,Y (powers of 1024) or KB,MB,... (powers of 1000).
デフォルトまたは --color=never を指定した場合、ファイルの種類を判別するための
カラー表示は無効となります。 --color=auto を指定した場合、標準出力が端末に接続
されている場合のみカラーコードを出力します。LS_COLORS 環境変数によって動作
を設定できます。LS_COLORS を設定する場合は dircolors を使用してください。
終了ステータス:
0 正常終了、
1 軽微な問題が発生 (例: 子ディレクトリにアクセスできない)、
2 重大な問題が発生 (例: コマンド引数が誤っている)。
GNU coreutils online help: <http://www.gnu.org/software/coreutils/>
ls の翻訳に関するバグは <http://translationproject.org/team/ja.html> に連絡してください。
Full documentation at: <http://www.gnu.org/software/coreutils/ls>
or available locally via: info '(coreutils) ls invocation'更新履歴
2017-07-28 Ubuntu 18.04 LTSで動作を確認
2017-10-27 Ubuntu 17.10で動作を確認

コメント